Adam Robert Dickerson. Credit Ally Lai.
ADAM ROBERT DICKERSON is the founder and artistic director of Fooju Dance Collaborative. Fooju began in 2014 as a cerebral playground for exploring what dance is and where it can happen. Engaging multiple disciplines and all the senses, Fooju's work takes place onstage, online, in public spaces, and in private homes. It is social, experimental, playful, messy, and often accidental. Dickerson has also choreographed works for the American College Dance Festival, the Youth America Grand Prix semifinals, the Colorado Springs Fine Arts Center, and musician RJD2. A former member of Graham 2 at the Martha Graham Dance Company, he currently dances with Amanda Selwyn Dance Theatre and Amy Marshall Dance Company.
“We want to make the chimerical intimately real.”
Odyssey Works: What is Fooju? How did it originate, and what is its purpose?
Adam Robert Dickerson: The name “Fooju” was birthed out of my own clumsiness. I mixed up “feng shui" and "juju," and just blurted it out. Immediately, I wanted the word to stick. The principle of accepting happenstance as creativity is central to my choreographic process: playful clumsiness gets refined into crafted dance. The word became an important reflection of my work.
Before officially beginning Fooju, I had worked closely for several years with my dance partner, Dolo McComb, at Colorado College. The work that we developed together as students there was the embryonic foundation for my future Fooju creations. After we graduated, Dolo moved to Minneapolis and I came to Brooklyn. Separate, yet forever choreographically tied, Dolo and I collaborated on a project we funded with Kickstarter in January 2015. Our long distance relationship fostered a new way of generating work together—through the Internet. By way of YouTube and FaceTime, we created an evening-length work, the first production under the name of Fooju Dance Collaborative. The performers, dancers and a few non-dancers, were a collection of my local friends and acquaintances, and would come to form the basis of the collaborative. We performed in a studio at the Martha Graham school, where several of us had trained, used Christmas lights as lighting, and invited audience members to drink and heckle us during the show and to donate objects to us in lieu of paying for tickets. Since then, Dolo has continued to create work in Minneapolis with with her own collective, //CATHEDRAL\\, while Fooju Dance Collaborative has grown in both size and vision under my direction in New York City.
Fooju Dance Collaborative is meant to frame the queerer qualities of existence by placing performative dance theatre outside the context of the proscenium; its purpose is to expressively and colorfully highlight the idiosyncrasies of the human experience. Fooju is the manipulation of visceral, incidental, or accidental creative impulses into dance that mimics the unconscious. We want to make the chimerical intimately real.
OW: How and why did the Works in Progresso series get started? What makes your kitchen shows different from typical dance performances, and what’s the point of doing things this way?
AD: Works in Progresso was borne of necessity. Producing a show in a traditional venue in New York City is prohibitively expensive for most choreographers, aside from the famous ones. More often than not, choreographers are losing money to create work, and significant profit is abnormal. So I made up my mind to make as much dance as I could manage without spending any money. The resources that were most readily available to me were my kitchen and my network of talented and willing friends.
I had long been choreographing, dancing, and filming dance videos in my kitchen, because the space was there. While looking towards developing a new full-length show last year, I had trouble finding a space. I eventually resolved to create work in my kitchen, for my kitchen. The goal was not to emulate concert dance in a kitchen, which would stretch the viewer's ability to suspend disbelief past its breaking point. Instead, my aim was to facilitate a harmonious, equal collaboration of hosts, choreographers, performers, photographers, videographers, and guests. I wanted to make the work specific to the venue, and to highlight our kitchen as the space where we make and share both meals and dances.
Lia Bentley and Adam Robert Dickerson dance in a kitchen. Dancer Vera Paganin and composer Wes Braver watch from "onstage;" Keenan Parry films. Credit Joe Desimone.
Once I decided to make a show with no budget, I began the rehearsal process at my apartment. My choreographic process was loose and quick. With most of the pieces, I gave my dancers a framework with few specifics. We embraced the chance of error. More often than not, the mistakes from a dancer’s body catalyze my choreography and lead it towards sincerity.
When we had a show ready, we invited our friends, bought a box of wine, and showed the work we had created together. The opening piece involved asking those watching for cookie recipes, and then baking a batch of cookies on the spot. Guests used their memories, phones, and collective tastes to contribute to the experience. This reliance on audience involvement initiated open communication between the "stage" and the viewers. The smell of the cookies gradually filled the room, until the oven timer sounded ten minutes into the dancing, and we served the audience warm cookies. We named the whole experience "Works in Progresso," an homage both to our home-brewed aesthetic and to the belief that all art is always a work in progress. We also served Progresso soup, although this was less popular than the cookies. Since then, we've brought various iterations of the Works in Progresso series to kitchens and living rooms throughout New York City.
“Stoking collaboration results in a splattering of new ideas onto what feels like a giant drawing board of new ways for dance to exist.”
OW: Why does Fooju involve performers and collaborators who work in disciplines other than dance? What do they bring to the table, and how do they change things?
AD: Collaboration ensures we have a varied array of talent under the Fooju umbrella, and it ties together differing modalities from each of the participating disciplines. We encourage all our artists to share their developing work with the group, and to present it at shows—so we all feed off of each other, and we all benefit from the experience of working with or around different mediums. In that way, Works in Progresso provides an opportunity for the artists in Fooju Dance Collaborative to experiment and share new ideas. This aspect of the series is what most compels me to continue curating shows for large and small audiences and to keep our collective motor running.
Stoking collaboration results in a splattering of new ideas onto what feels like a giant drawing board of new ways for dance to exist. Every show is different. We always throw in new pieces and complete re-workings of old pieces. We are often still playing around with things right up until our audience arrives! The “trial and error” mentality of Fooju amplifies our energy and makes us feel as if we are dancing out into the unknown with each new show.
Fooju not only serves as a source of mutual experimentation and inspiration for our members, but it has also become something of a support group for those of us with questions about how to navigate the performing arts world. Also, I enjoy the wider audience and increased opportunities that naturally follow a more diverse group. This has proven helpful to us in connecting with prospective collaborators and hosts.
OW: Your kitchen shows take place in small, semi-private spaces amongst people who mostly know each other; the dancers and audience members intermingle. At these events, where do you draw the line between a dance party and a dance performance? Between the artists and the audience? Where is the artwork itself located?
AD: Fooju’s Works in Progresso series is an invitation for showgoers to unlearn audience etiquette, and for our performers to unlearn stage etiquette. We are still testing and determining the boundary between the audience and the performers, but it is definitely porous. Those who keep coming back to our shows are just beginning to understand the fluidity of roles we embrace. Our performers watch the show—sometimes with our guests and sometimes from within the designated performance space—during the pieces they are not in. Fooju performers are also encouraged to include the audience in their performances, just as a host includes their guests in conversation.
Deciding to put dance in a kitchen generated many questions for us about the meanings of terms like "audience," "dancer," and "stage." We are constantly in the process of deciding which performance conventions we want to keep, which we want to modify, and which we want to discard. Generally, we do engage the traditions of lighting, music, and a suggested area for the dancing to take place.
Yet we do not pretend to be in a theatre. Our events are free of charge and involve food, drink, and socializing before, after, and even during the show. We do usually lose track of where the show ends and the party begins and where the party ends and the show begins. We have a running joke where whenever anyone asks when the performance is starting, we say "The show already started! This has all been the show!" Works in Progresso is, in fact, about the multi-faceted magic of the entire experience. Dance is something we like to do among friends and new acquaintances, not something we want to present to strangers. We see it as a social gift that we will share with anyone generous enough to receive it. We work to maintain the honesty of being "at home."
However, it is important to us to still create a theatrical, heightened experience. This is more, not less, possible in a kitchen than in a theatre. Whatever we might lose from not being on a stage, we gain back tenfold from being in our own sacred spaces. Having a show in an a small, private space yields qualities of intimacy similar to a religious ritual or ceremony. I choose to highlight these qualities by asking the audience to wear party hats for unity and drink our special (alcoholic) Foojuice. We begin each show by smudging the space and annointing the performers with glitter face paint. A Fooju show is a quiet spectacle, like a dream.
Adam spreads glitter on dancer Anna Zekan's face before a show in Astoria. Credit Joe Desimone.
OW: Fooju relies heavily on technology. Earlier projects have included Photobooth Ballet and Kitschy Kitchen, both video series. All your shows are recorded, and you encourage performers and audience members to use social media during each performance for documentary and promotional purposes. What does all this mean in the context of an art form founded on liveness?
AD: As with dancing in people's homes, lack of funds were the initial impetus for the use of technology in my work. YouTube and social media are free, and almost everyone I know has a phone with a camera on it. Technology also enables the members of Fooju to collaborate long distance and without having to always set aside time to all meet together in person. It is such an easy tool for creating and sharing work. Beyond that, when audience members post on social media, it brings Fooju beyond the boundaries of the performance space. It allows them to perpetuate the performance by putting their own creative take on what they see and experience. It's one more means of inviting the audience to collaborate with us.
While live dance will always be the genesis of my process, I have also always been passionate about film as a way to structure and frame movement. Keenan Parry has been Fooju's resident filmmaker from the beginning, and his artistry with the camera complements my choreography well. His delightfully playful cinematography highlights new dimensions of the dancing that may not have been as apparent during the live performance. He does not document the art, but co-creates it with us. He's also an integral part of our live performances. In our more recent shows, he has dressed in a green screen suit and followed dancers around the apartment with his camera. He's not quite audience member, not quite dancer, but something of a transitional object.
“I trust my unconscious, so I rely on chance and circumstance to sift through choreographic choices, allowing mishaps and obstacles to make decisions for me.”
OW: Who are your influences, and within what aesthetic and conceptual traditions do you locate your work?
AD: My exposure to collaborative theatre groups such as Elevator Repair Service and Forced Entertainment has influenced my sense of humor and my way of using found movement and improvisation to lay a foundation for my work. Eiko & Koma have inspired my use of time and imagination to modulate my choreography. Elements of Pina Bausch often find their way into Fooju shows: large choruses of dancers, quasi-pedestrian choreography, vocalization, and seemingly disconnected vignettes. Finally, my passion for the legacy of Martha Graham was what initially brought me to New York to study at the Martha Graham School of Contemporary Dance and dance with the Graham 2 company; this is the foundation of my dance technique and my choreography.
On the theoretical side of things, I draw from Antonin Artaud’s idea of the dream aesthetic and Richard Schechner’s insights on ceremony. I am a romantic surrealist with hopes of physicalizing and ritualizing the queerness I experience in my dreams. I trust my unconscious, so I rely on chance and circumstance to sift through choreographic choices, allowing mishaps and obstacles to make decisions for me. If the language of dreams and the language of movement are universal, my aim is to resonate with the unconscious language of the individual. That’s you! And that’s Fooju.
...................
Interview by Ana Freeman












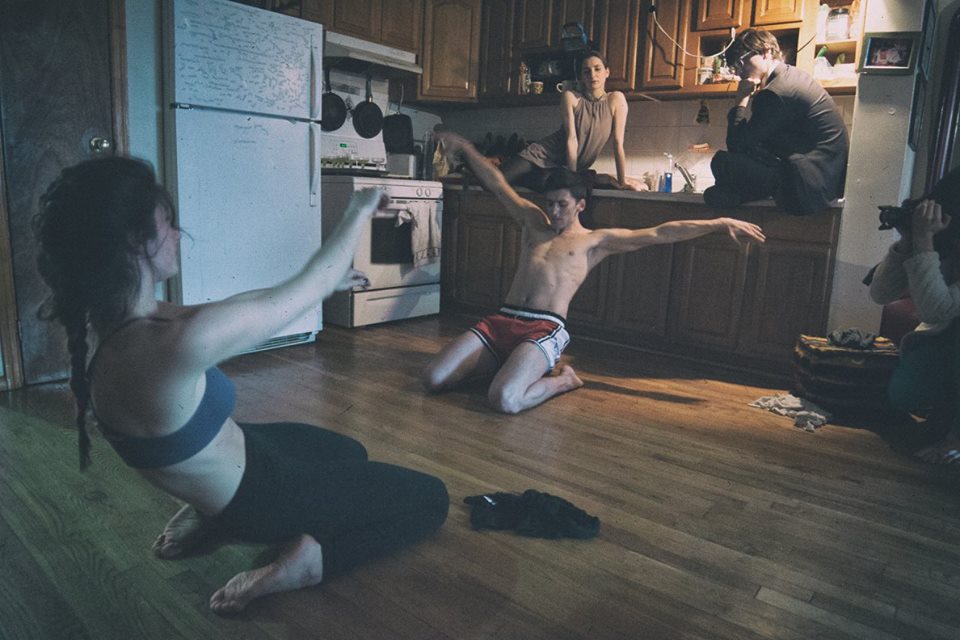




That is, I believe, why I read poetry and seek out jarring art: for a cognitive sneak attack that tricks me into thinking in new ways. It is also why the smart, minimal, dark, rhythmic, unexpected staging of New Paradise Laboratory’s Hello Blackout! won’t leave me alone even now, a month after my having seen it. The piece was choreographed to trick me into thinking in a feeling-being-melancholic way about some big ideas.